
ASPIRE
Computing

We aim to achieve a high-quality curriculum that will equip our students to use computational thinking and creativity. This will enable them to see, understand and be part of change across the world in future generations.
The curriculum contains three main parts, Digital Literacy, IT and Computer Science which constitutes the KS3 National Curriculum. Together these topic areas are used to build solutions linking both natural and artificial systems. Developing this knowledge and understanding, students are able to design and create programs, systems and associated content using IT in the classroom.
At the end of KS3 students may choose from GCSE Computer Science and or the vocational qualification OCR Creative i-media.
Implementation
Programmes of study
Year 7
In Year 7 students focus on the fundamental concepts and principles of computer science, using computational thinking in a variety of situations. They study online / e-safety, word processing and excel skills, research skills and the use of Scratch a block - based programming language to learn the fundamentals of programming.
Year 8
In Year 8 students develop their computational thinking skills which is strengthened by the capacity to solve problems in a variety of situations. They will study binary, vector graphics using Inkscape, computer systems considering hardware and software, machine learning and artificial intelligence and an introduction and the text -based programming language of Python
Year 9
During Year 9 there is an ongoing development of skills from Years 7 and 8. Students start to consider algorithmic thinking using flow charts to further strengthen programming outcomes. A deeper understanding of cyber security is acquired and a more in -depth approach to the text -based programming language of Python and the impact of technology on today’s society.
GCSE Computer Science
Year 10
In Year 10 students follow the OCR J277 Computer Science course of study which culminates in sitting two examination papers both of which are 90 minutes long at the end of Year 11.
Students will focus on computer systems and computational thinking, algorithms and programming are covered in across the examination papers.
Year 11
During this year students follow the J277 specification of OCR GCSE Computer Science. This is assessed terminally with two examination papers. This year provides for a development of a deeper understanding of the topics from year 10, preparation of revision materials and practising key concepts.
Marking and Assessment
Formal assessment takes place at the end of each topic area combined with interim tests conducted in examination conditions. Regular feedback is given to students in line with the West Craven Marking policy. Self and peer evaluations takes place frequently.
Examinations
Component 01: Computer systems
Introduces students to the central processing unit (CPU), computer memory and storage, data representation, wired and wireless networks, network topologies, system security and system software. It also looks at ethical, legal, cultural and environmental concerns associated with computer science.
Component 02: Computational thinking, algorithms and programming
Students apply knowledge and understanding gained in component 01. They develop skills and understanding in computational thinking: algorithms, programming techniques, producing robust programs, computational logic and translators.
Practical programming
Students are to be given the opportunity to undertake a programming task(s) during their course of study which allows them to develop their skills to design, write, test and refine programs using a high-level programming language. Students will be assessed on these skills during the written examinations, in particular component 02 (section B).
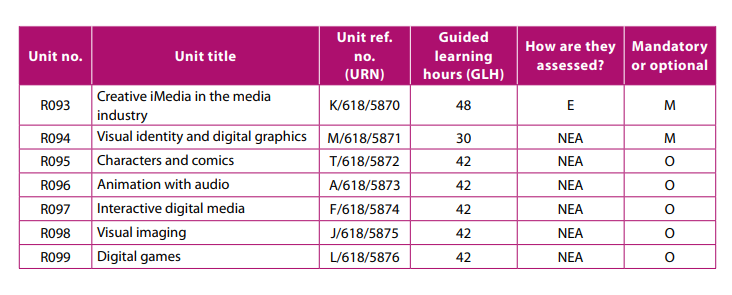
OCR Creative i-media
Year 10
Throughout Year 10 students will be developing their knowledge of RO93, the examined assessment. They will undertake assessments of RO93 throughout the year including a mock examination at the end of Year 10. This examination is sat at the end of Year 11. They also need to prepare and complete the mandatory assessment RO94 which has to be submitted at the end of Year 10.
Year 11
During this year students will continue to develop their subject knowledge for RO93 undertaking half termly summative tests and a mocks in October and February to prepare them for the final external examination in May 2024. They also need to complete RO97 a non -examined assessment that has been chosen by the class teacher. The grades for this will also be submitted in May 2024.
Careers and Progression
With technology becoming a pivotal part of our everyday existence, it is no surprise that jobs are in demand in this sector. Having a solid understanding and knowledge of computer technology is hugely beneficial as your expertise is not only necessary, but it could lead you towards a well-paid job.
The essential elements of computer science is to design, develop, and problem-solve. Computational thinking is the approach you need to take when working in a computer science-related role.
Studying GCSE Computer Science will allow progression to A level and university and vocational courses. There are a number of careers in this sector some of which are shown below.
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Application Analyst
- Forensic Computer Analyst
- Applications Developer
- Database Administrator
- Game Designer
- Forensic Computer Analyst
- Games Developer
Revision Guides / Resources
CGP GCSE Computer Science OCR Revision Guide
Cambridge University Press OCR imedia Revision Guide
Learning Journeys
Year 7 Computing Learning Journey
Year 8 Computing Learning Journey
Year 9 Computing Learning Journey
To find out more about our Computing curriculum, please contact Ms N Hussain, Head of Computing, by emailing nhussain@westcraven.co.uk or phoning the main office to arrange a call back.